Borrowing costs are interest and other charges that must be paid by companies that borrow money (debitors). Long-term borrowings in corporate finance practices are included in financing activities. Long-term borrowings should be used to fund investing activities, not operating activities. In the financial statements, investing activities are reflected in the non-current assets section, while operating activities are reflected in the company’s current assets and statement of profit and loss.
Table of Contents
Financing activities from the corporate finance side can be carried out through debt financing and equity financing. Debt financing can be obtained from bank loans, bond issuance, and debt securities in the capital market. Companies need to calculate the cost of capital on borrowings in the valuation of an investment or business.

Valuation Methods for Borrowing Costs
One of the generally accepted valuation methods is the revenue approach, by considering the Free Cash Flow that a company, can be obtained during the projected income period in the calculation. This calculation involves the rate of return expected by the lender and factors in the time value of money.
The valuation of borrowing costs considers the risk of the lender’s for cost of capital, as investors pursue the maximum rate of return on the money they have lent. Common forms of loan instruments and loan cost calculations are as follows:
Valuation of Borrowing Costs for Different Instruments
Bonds
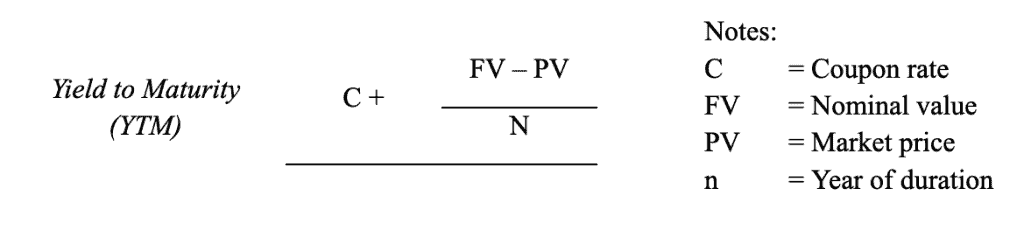
Bonds are securities issued as tokens of debt to bondholders or investors. Usually, bonds are issued by the government and business entities, with the duration of medium or long term. Debt costs incurred on bond ownership are in the form of Yield to Maturity, which represents the rate of return until the bond matures with the following formula:
Bank Loan
Companies can obtain loans from banks, both government banks and private banks, for various purposes of using funds, including for working capital and investment needs. The application of the use of the cost of capital for bank loans in general comes from market interest rate data from the average bank that carries out the financing function. This data can be accessed through the websites of the Financial Services Authority (OJK), the Central Bureau of Statistics (BPS), and other government agencies.
Commercial Paper
Commercial Papers are money market securities, both in the form of promissory notes, checks, time deposits, and notes of acceptance, both issued by large capitalized banks and companies. The term of the instrument is usually short-term (less than 9 months) for the purpose of working capital management. The approach to calculating the cost of capital for commercial securities is the implicit interest rate with the following formula:
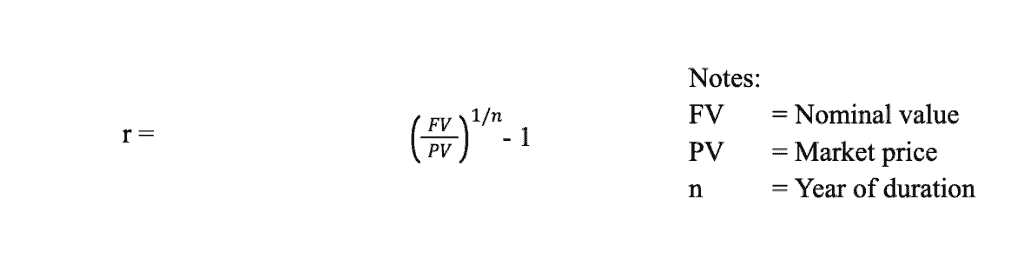
The Mix of Borrowing Instruments
Conditions in which the company has various debt instruments in terms of financing methods, both working capital and investment, are calculated using the weighted average method. The cost of capital is calculated by the following formula:
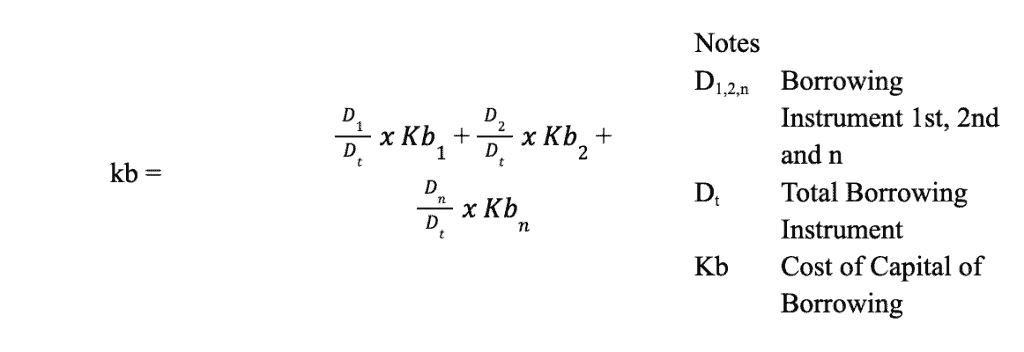
Considering Feasibility, Tax, and Accounting Treatment
The company needs to evaluate whether the loan is a feasible solution to take. In addition to the valuation of borrowing costs, companies need to understand the tax and accounting treatment for borrowing costs. Economic decisions become more comprehensive after understanding the valuation of feasibility, tax regulations, and financial accounting standards for borrowing costs, plus how audit procedures will be carried out by their independent auditors.
If you’re seeking expert guidance on the valuation of borrowing costs in Indonesia, look no further than SW Indonesia. Our team of financial professionals is equipped with in-depth knowledge and extensive experience to assist you in navigating the complexities of corporate finance. Whether you require valuation services or need to optimize borrowing costs, we are here to support your financial endeavors. Contact us today at +62 2993 2132 to unlock the full potential of your business and make well-informed decisions that drive success.













